2025: The Year of Browser Bugs
In the beginning of this year, we launched the Year of Browser Bugs (YOBB) project , a commitment to research and share critical architectural vulnerabilities in the browser. Inspired by the iconic Months of Bugs tradition in the 2000s, YOBB was started with a similar purpose - to drive awareness and discussion around key security gaps and emerging threats in the browser.
Over the past decade, the browser has become the new endpoint, the primary through which employees access SaaS apps, interact with sensitive data, and use the internet. The modern browser has also evolved significantly, with many capabilities that support complex web apps that parallel the performance of native apps. As with all new technologies, the very same features are also being used by malicious actors to exploit users, exploiting a massive security gap left by traditional solutions that primarily focus on endpoints and networks. Compounded with the release of AI Browsers, the browser has become the single most common initial access point for attackers. Yet, it remains to be poorly understood.
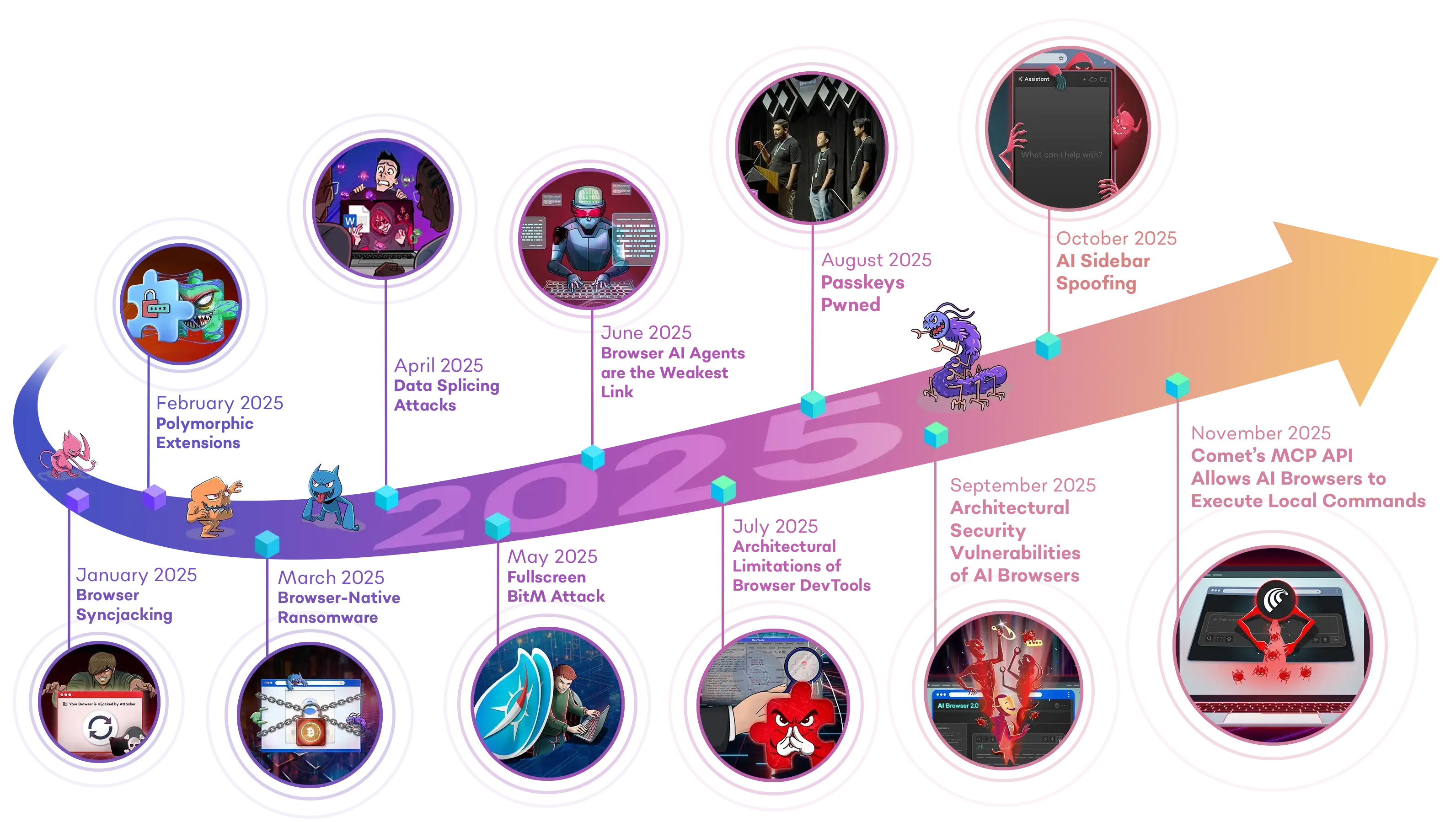
The YOBB project aims to demystify these vulnerabilities, by highlighting architectural limitations, behavioral trends and industry dynamics that cannot be fixed by a simple security patch. In the past 12 months, we released 11 research pieces, including major zero day vulnerabilities presented at DEF CON, BlackHat, RSA and BSides. Here is a recap of our findings:
Security Research Exposés

Comet’s MCP API Allows AI Browsers to Execute Local Commands
November 2025
Our research reveals that Comet has implemented an MCP API that allows its embedded extensions to execute arbitrary local commands on host devices without explicit user permission, including executing known ransomwares.
Learn More
AI Sidebar Spoofing
October 2025
In the AI Sidebar Spoofing attack, a malicious extension impersonates Comet’s AI sidebar, tricking users to navigate to malicious websites, run data exfiltration commands and even install backdoors that provide attackers with persistent remote access to the victim’s entire machine.
Learn More
Architectural Security Vulnerabilities of AI Browsers
September 2025
As AI Browsers rapidly gain adoption across enterprises, SquareX released critical security research exposing major vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to exploit AI Browsers to exfiltrate sensitive data, distribute malware and gain unauthorized access to enterprise SaaS apps.
Learn More
Passkeys Pwned: Turning WebAuthn Against Itself
August 2025
The Passkeys Pwned attack highlights a passkey implementation flaw, specifically that of WebAuthn in the registration and authentication process, allowing unauthorized access to enterprise SaaS apps and resources.
Learn More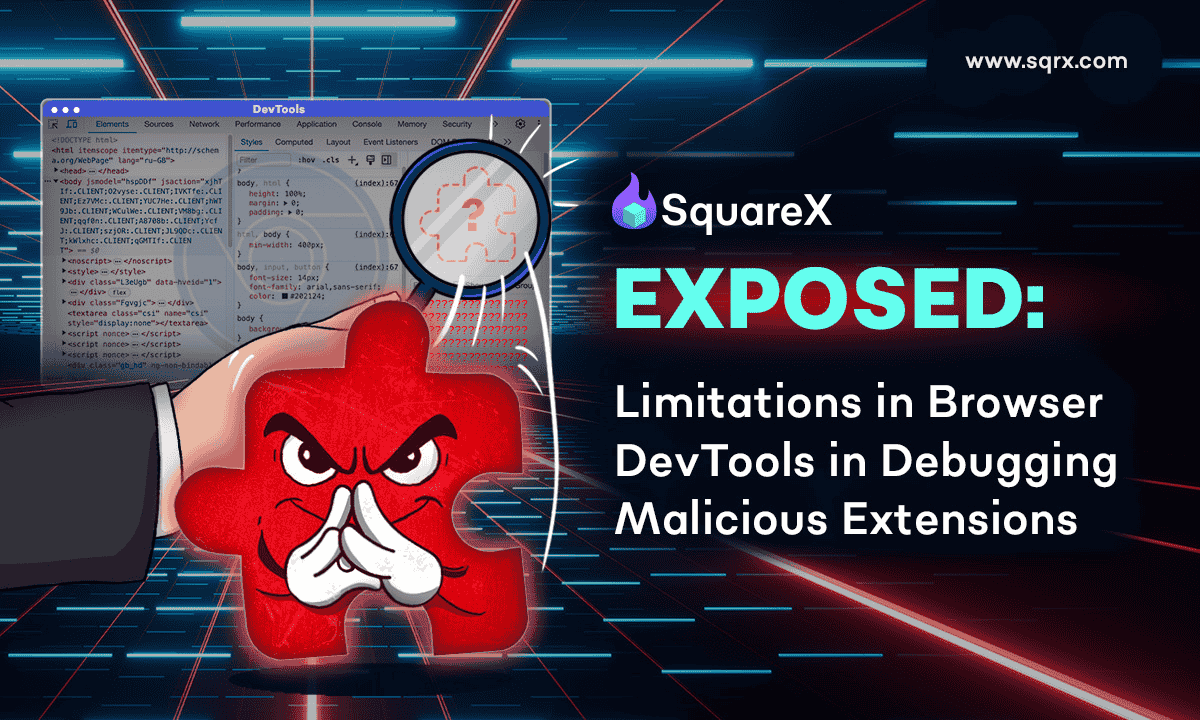
Architectural Limitations of Browser DevTools
July 2025
Despite the expanding use of browser extensions, it is impossible for browser vendors and businesses to debug extensions with existing Browser DevTools. Existing DevTools were designed to inspect web pages, and are unable to capture complex and dynamic extension behaviors at runtime. SquareX’s Extension Analysis Framework enables enterprises to assess an extension's security risk with metadata analysis, advanced static code analysis and dynamic analysis.
Learn More
Browser AI Agents: The New 'Weakest Link'
June 2025
79% of organizations use Browser AI Agents. These AI agents are more vulnerable to attacks than human employees, making them the new weakest link in enterprise security.
Learn More
Fullscreen BitM Attack
May 2025
With a single click, victims can trigger a fullscreen Browser-in-the-Middle (BitM) window. Unaware that they are now interacting with an attacker-controlled browser, the victim enters their credentials and conducts their work while being fully monitored by the attacker. Although this attack applies to all browsers, Safari users are especially vulnerable to this attack as there is no clear visual indicator of users entering fullscreen.
Learn More
Data Splicing Attacks
April 2025
First unveiled at BSides San Francisco 2025, Data Splicing Attacks are a new class of data exfiltration techniques that completely bypass major Data Loss Protection (DLP), SASE and SSE vendors listed by Gartner, by exploiting architectural vulnerabilities in the browser.
Learn More
Browser-Native Ransomware
March 2025
As we move towards a cloud and SaaS-centric workplace, browsers are becoming the new endpoint. The discovery of browser-native ransomware provides a glimpse to the evolution of ransomware - one which renders EDRs obsolete, putting millions of organizations at risk.
Learn More
Polymorphic Extensions
February 2025
Polymorphic extensions impersonate legitimate extensions such as password managers and crypto wallets, leading victims to believe that they are providing credentials to the real extension.
Learn More
Browser Syncjacking
January 2025
Browser Syncjacking is a new attack technique where a single malicious extension can be used to completely hijack the browser, and eventually, the whole device.
Learn More
OAuth Consent Grant Phishing
December 2024
SquareX was the first to sound the alarm on OAuth-based consent grant attacks behind the Cyberhaven breach. These attacks targeted Chrome extension developers, where threat actors used phishing emails to gain access to developers' Chrome Store accounts and push malicious updates to users.
Learn More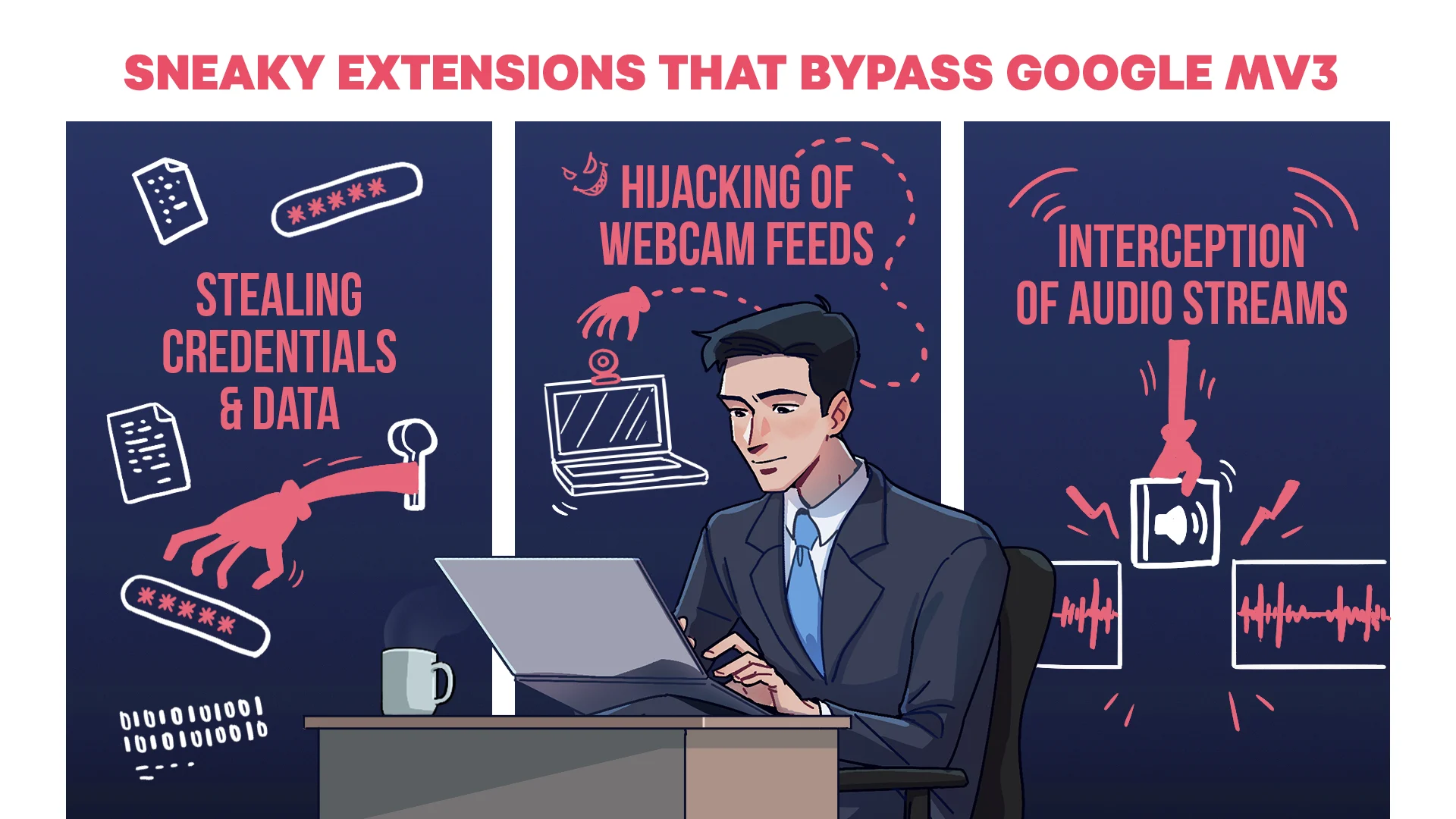
Sneaky Extensions: MV3 Vulnerabilities
October 2024
The SquareX team demonstrated how despite Google MV3's improved security controls, malicious extensions can still bypass MV3's security controls to compromise users.
Learn More
Last Mile Reassembly Attacks
August 2024
On the DEF CON 32 main stage, SquareX unveiled Last Mile Reassembly Attacks.

SquareX finds security flaws in top email providers
April 2024
SquareX researchers highlighted that top email providers including Apple, Gmail, Microsoft, and Yahoo - which billions use - failed to detect and block malicious attachments.
Learn More
